单体可重构的电动汽车动力电池包结构设计(含CAD图,STP三维图)(任务书,开题报告,文献摘要,论文说明书21000字,CAD图3张,STP三维图)
摘要
电动汽车高速发展的今天,动力电池系统作为其发展的关键和瓶颈,技术研发上也不断地取得突破。正是因为动力电池的重要地位,其结构设计上关系到整体系统的各项性能特点和安全要求,进而影响到整车的综合表现。本文根据课题组内对设计车辆的整车要求以及对动力电池的参数要求,完成电动汽车动力电池包的结构设计和相应的特性分析工作。
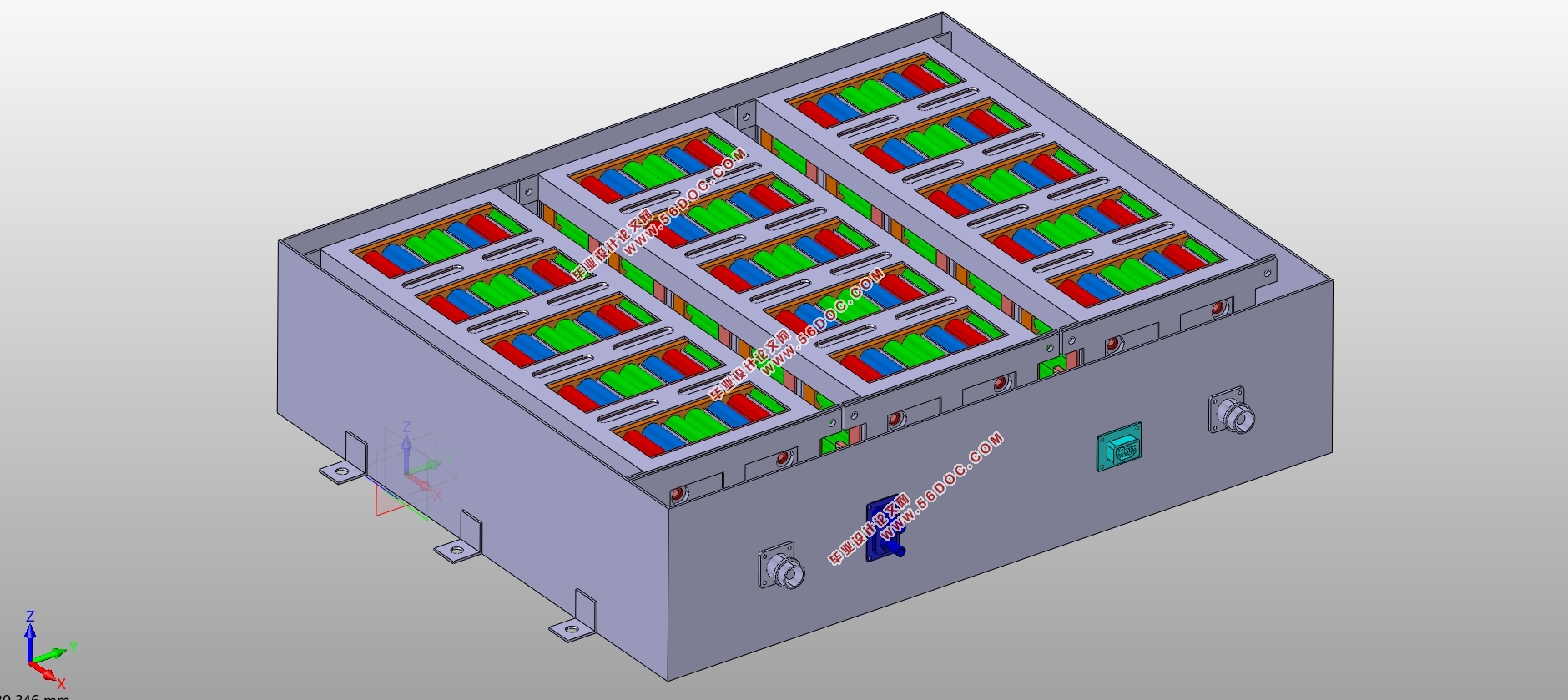
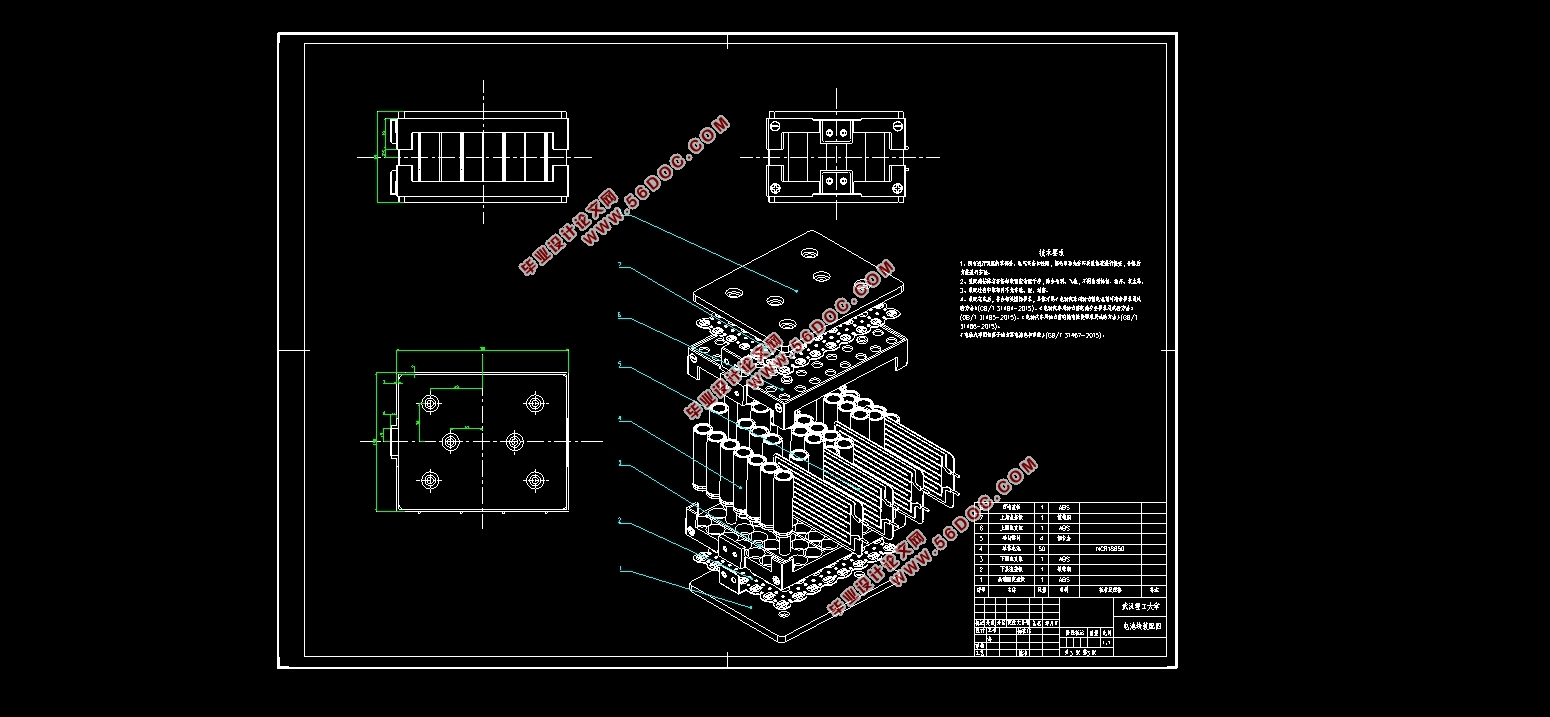
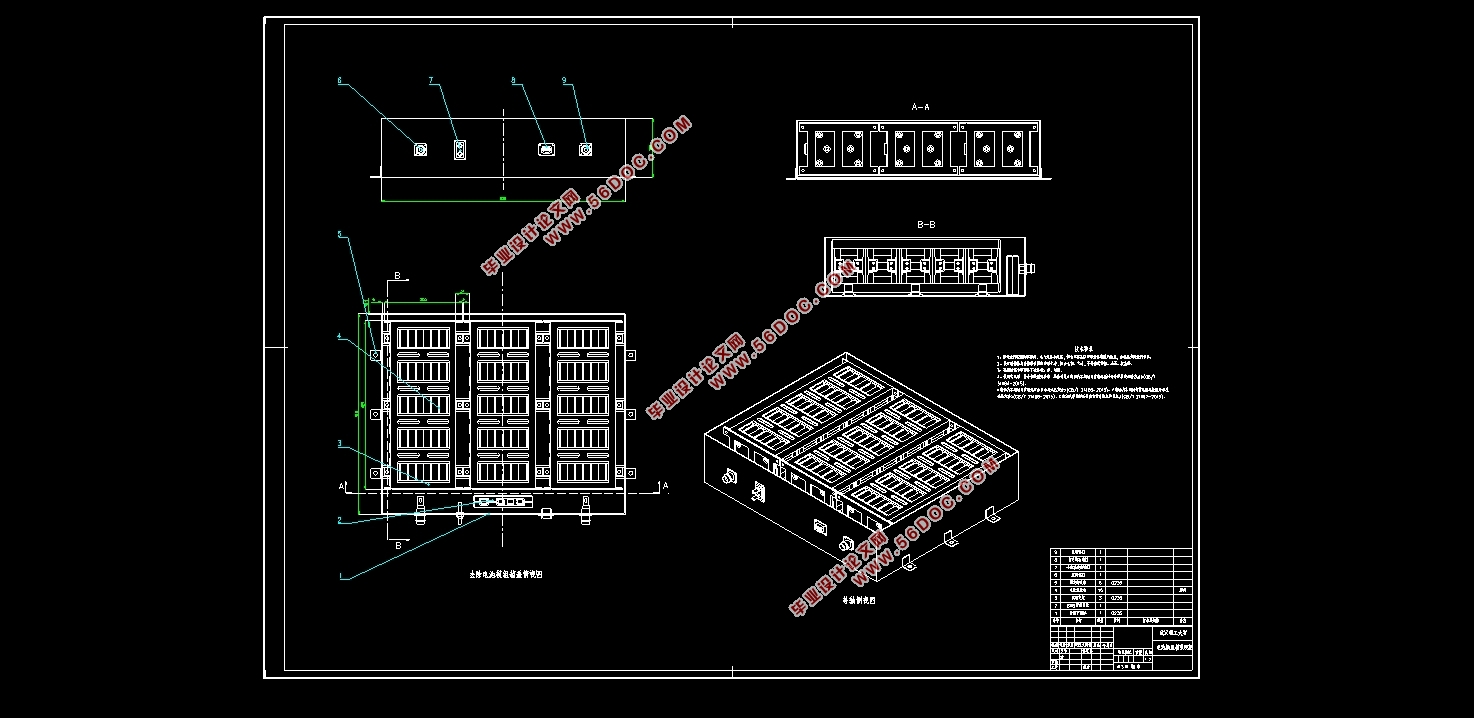
首先,本文分析动力电池包设计过程中必须满足的各项安全性要求,确定采用3750个NCR18650型锂离子电池单体,通过50并75串的结构形式构成动力电池包的基本框架。电池包系统整体电池容量达到设计要求的36.5kW•h,电池总电压为270V,验算其满足理论上最大续航里程达到240km。动力电池包内部结构为5个相同规格的电池模组箱体呈异形T字排布,采用液体散热的冷却方式,防水防尘密闭等级为IP67级,安装于汽车底盘下方,车架纵梁跨度之间。所设计得电池包的总质量预估为364.382kg,计算得功率密度达到555.74 W/kg,基本满足设计要求的包级功率密度目标要求。
其次,完成对所设计的动力电池包进行结构特性分析和校验。运用CATIA三维建模软件完成动力电池从单体级到模组级再到整体包级的实体建模,结合ANSYS有限元分析软件分析验证颠簸+紧急制动、颠簸+紧急转弯两种典型组合工况下动力电池包的结构强度,在ANSYS Workbench平台进行电池包的自由模态强度分析。阐述当前电动汽车在碰撞性能上的要求,碰撞测试的必要性;结合安装位置和结构设计特点,分析了电池包各个方面的防碰撞措施,并模拟纯电动汽车侧面碰撞情景,运用LS-DYNA求解器和LS-PrePost软件对电池包进行模拟侧面碰撞分析。
最后,介绍未来动力电池随着性能的下降,使用寿命到达上限,将会有大量的电池退役报废,当前动力电池循环回收利用上前景广阔;分析目前热点研究话题——“快速换电”的突出优势和面临的难题;结合上述现象重点分析了所设计的电池包可重组可重构性。
关键词:电动汽车;动力电池;结构设计;强度校验;碰撞性能;单体重构
Abstract
With the rapid development of pure electric vehicles, power battery system is the key of its development, and breakthroughs have been made in technology research and development. Because of the important position of power battery, its structure design is related to the performance characteristics and safety requirements of the whole system, and then affects the comprehensive performance of the vehicle. In this paper, according to the requirements of vehicle design and parameters of power battery, the structure design and corresponding characteristics analysis of power battery pack for pure electric vehicle are completed.
Firstly, this paper analyses the safety requirements that must be met in the design process of power battery pack, and determines that 3750 NCR 18650 lithium-ion battery monomers are used to form the basic framework of power battery pack through 50 and 75 series structure. The overall battery capacity of the battery pack system meets the design requirement of 36.5kW• h, and the total battery voltage is 270V. The theoretical maximum endurance range of the battery pack system is 240 km. The internal structure of the power battery pack is five battery module boxes of the same specifications arranged in a special T-shaped arrangement. The cooling method of liquid heat dissipation is adopted. The waterproof and dust-proof sealing grade is IP67. The power battery pack is installed under the chassis of the automobile, and the span of the longitudinal beam of the frame is between. Basically meet the design objectives. The total mass of the designed battery pack is estimated to be 364.382 kg, and the calculated power density reaches 555.74 W/kg, which basically meets the design requirements of the package level power density target.
Secondly, the structural characteristics of the power battery pack are analyzed and verified. CATIA three-dimensional modeling software is used to complete the solid modeling of power battery from single level to module level and then to whole package level. The structural strength of power battery pack under two typical combined working conditions of bump+emergency braking and bump+emergency turning is verified by ANSYS finite element analysis software. The free mode strength analysis of power battery pack is carried out on ANSYS Workbench platform. The requirement of collision performance and the necessity of collision test for electric vehicle are expounded. Combining with installation position and structural design characteristics, anti-collision measures in all aspects of battery pack are analyzed, and side collision scenario of pure electric vehicle is simulated. LS-DYNA solver and LS-PrePost software are used to simulate side collision analysis of battery pack.
Finally, with the performance degradation and service life reaching the upper limit, a large number of power batteries will be decommissioned and discarded in the future, and there will be broad prospects for recycling and utilization of power batteries at present. The outstanding advantages and difficulties of the current hot research topic - "rapid power change" are analyzed, and the reconfigurability of the designed battery pack is emphatically analyzed combined with the above phenomena.
Key Words:pure electric vehicle; power battery; structural design; strength check; collision performance; single body reconstruction.
本论文主要研究内容以及具体任务包括以下三个:
(1)根据电动汽车的主要性能参数以及动力电池包的参数要求进行动力电池包的结构设计,电池分为包级-模组级-单体级,主要完成电池包各大组成构件的设计,包括模组结构、电池包结构、壳体结构等以及所有组件结构设计、连接方式确定;
(2)动力电池包结构特性分析,合理的结构设计关系到整体电池包的各项性能指标和安全要求,在设计电池包结构过程中,要最大限度的避免制造使用时带来不必要的麻烦,因此主要研究在复杂工况下所设计的电池包具有的结构强度,即静力学条件下,电池箱体的强度校验,进行自由模态分析以及碰撞性能的分析,模拟碰撞情形指出碰撞下电池包的保护措施和未来的优化方向;
(3)设计的电池包必须可拆解,单体可重组,易于可循环再利用,动力电池结构设计过程中注重单体可重构性的考虑和体现,实现电池单体级的循环利用,节约资源,并有利于电池包拆装、各级更换、系统维修。
2.1结构设计基本要求
2.1.1 整车设计要求
同内燃机在传统能源汽车上的作用一样,电池是新能源汽车的动力源,其重要意义不言而喻[8]。在电池包结构设计之前首要确定的就是整车的设计要求以及确定电池包的基本性能参数要求,也为电池系统的参数匹配工作建立方向,为后续结构的具体设计打下基础。
本课题设计对象为一款纯电动汽车,其整车设计要求如下:
(1)车型为一款越野车,具有四轮分布式驱动功能;
(2)轮毂驱动单元采用电机加轮边减速机形式,轮边减速机采用行星传动机构,单级减速;
(3)整车最高速度为120km/h;
(4)最大续驶里程为240km;
(5)单电机额定功率为20kW,额定转速为3600rev/min;
(6)乘员数为5人,五门;
(7)电池为锂电池,电池容量36.5kW•h,功率密度不小于200W/kg(包级);
(8)长宽高为4585mm×1855mm×1679mm;
(9)轴距2660mm;
(10)最小转弯半径5500mm。
在设计过程中,课题组内设计需要用到的相关参数要求如下表2.1所示:
表2.1整车设计相关参数
参数 数值 参数 数值
车重/kg 1850 空气阻尼系数/(N•S²/m4) 0.40
滚动阻尼系数 0.012 迎风面积/m2 3.098
传动效率 0.92 平均车速(km/h) 50

目 录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第1章绪论 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2 动力电池包研究现状 1
1.2.1 动力电池发展现状 1
1.2.2 动力电池包结构设计研究现状 2
1.3 论文主要研究内容 5
第2章 动力电池包结构设计 6
2.1 结构设计基本要求 6
2.1.1 整车设计要求 6
2.1.2 安全设计要求 6
2.2 动力电池包系统参数匹配设计 7
2.2.1 单体选型 7
2.2.2 电池容量校核 8
2.2.3 电池电压设计 9
2.2.4 电池系统框架结构设计 10
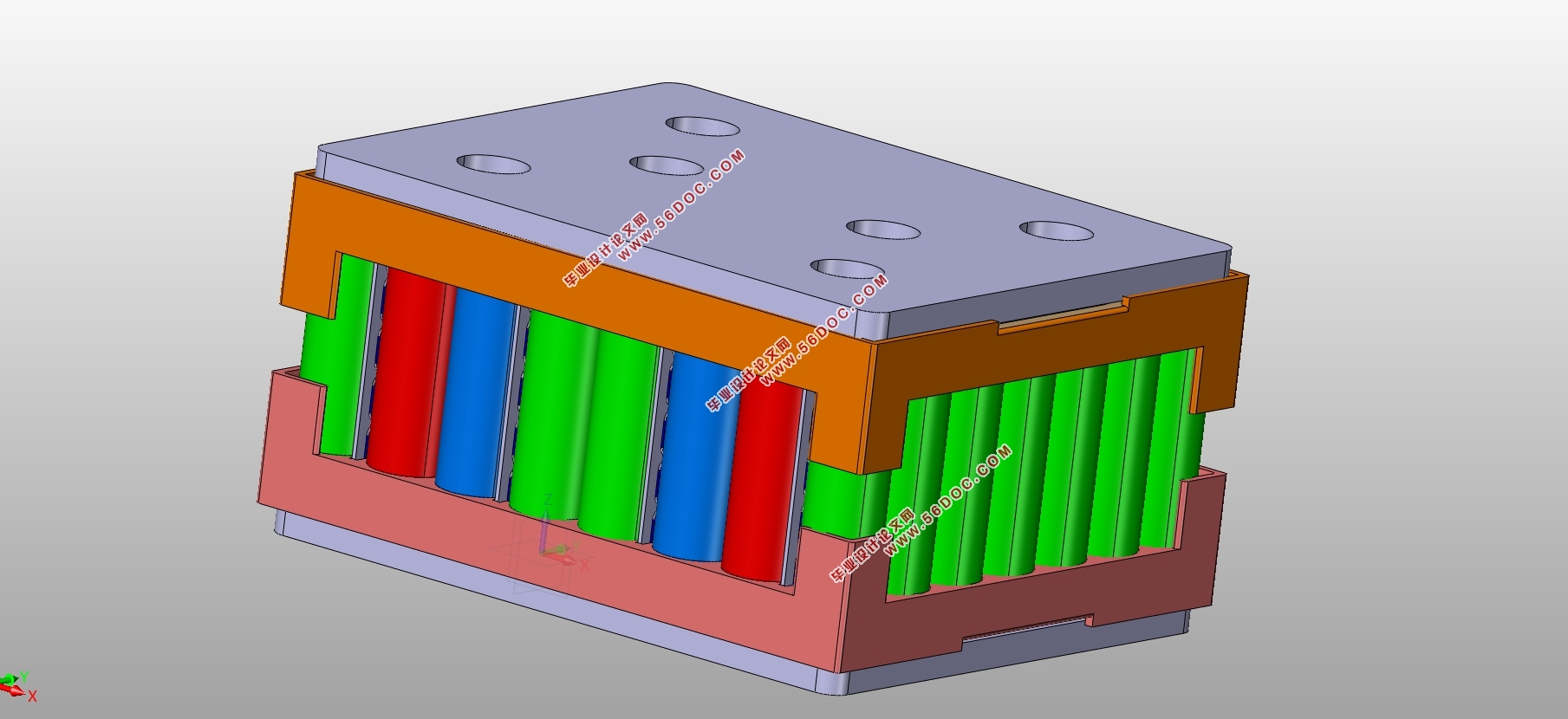
2.3 电池模组结构设计 11
2.3.1 单体布置方式选择 11
2.3.2 冷却方式比较及选择 12
2.3.3 电池块结构设计 13
2.3.4 电池模组成组设计 16
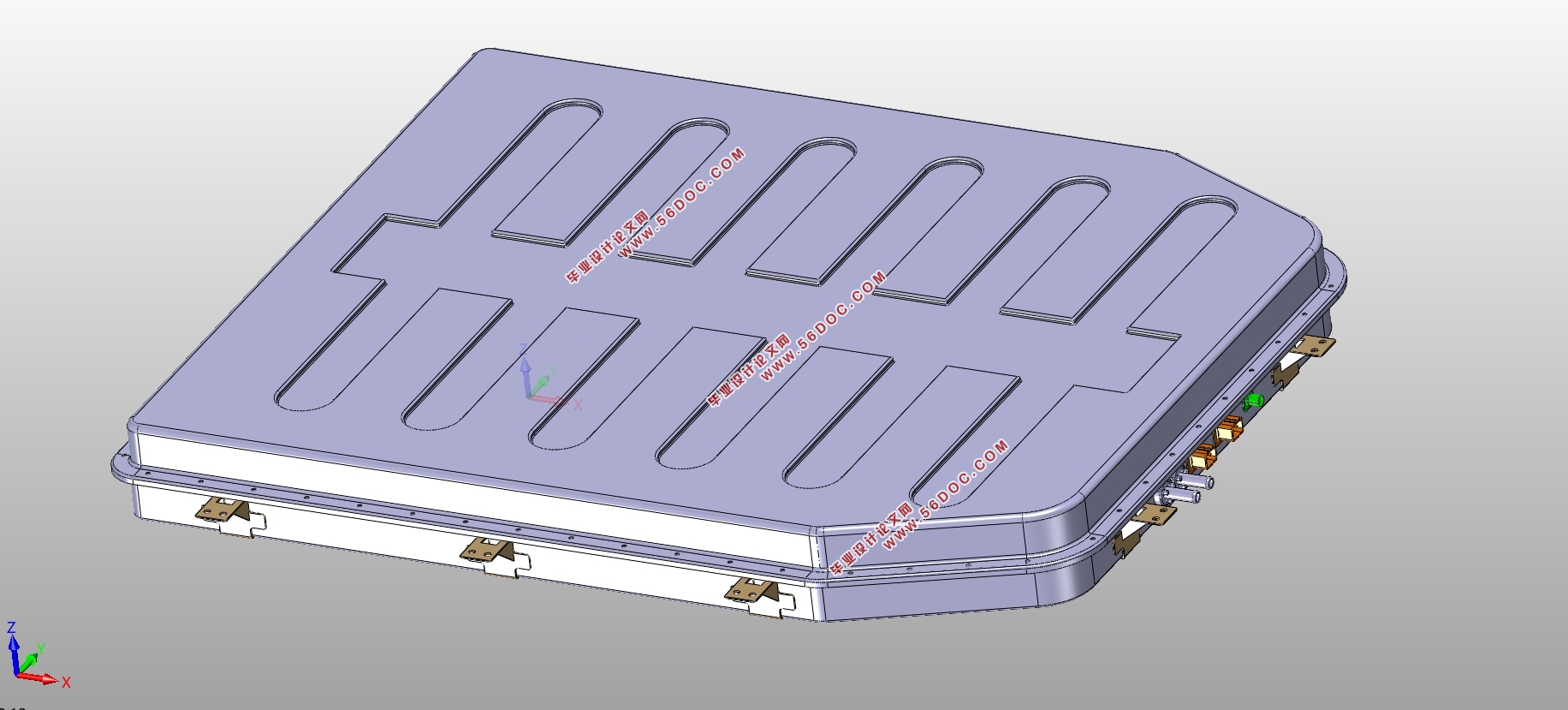
2.4 电池包结构设计 19
2.4.1 安装位置确定 19
2.4.2 模组布置方式 19
2.4.3 壳体结构设计 20
2.4.4 连接方式确定 20
2.5 其他组件设计 22
2.6 动力电池包功率密度计算 23
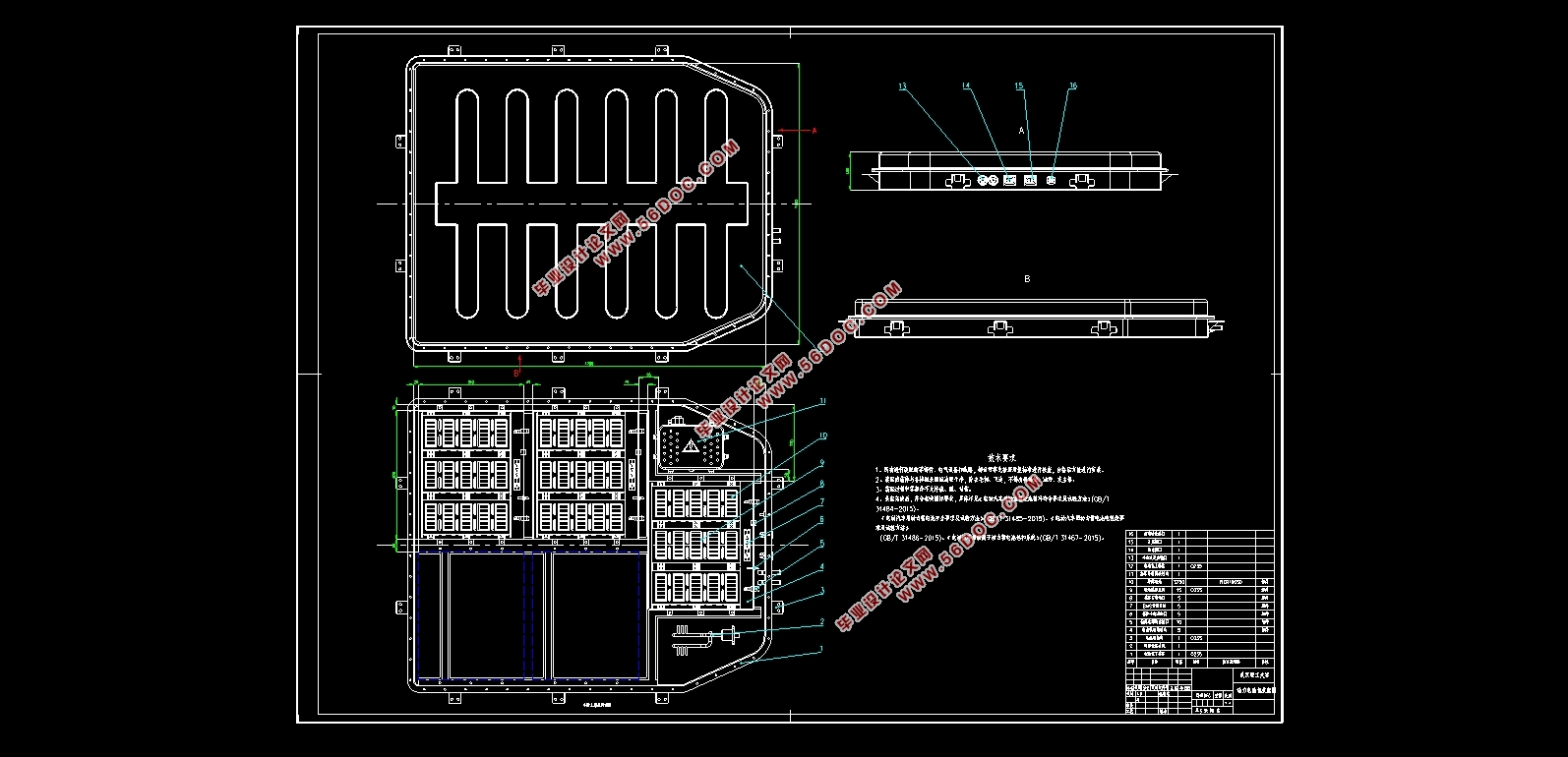
2.7 动力电池包结构总览 24
第3章动力电池包性能有限元分析 25
3.1 电池包有限元分析 25
3.2 模型建立与分析手段概述 25
3.3 动力电池包强度分析 26
3.3.1 典型工况下的电池包结构强度分析 26
3.3.2 动力电池包模态分析 28
3.4 动力电池包碰撞性能分析 30
3.4.1 碰撞测试与碰撞防护分析 30
3.4.2 侧面碰撞情景分析 31
第4章动力电池包单体可重构分析 34
4.1 动力电池回收利用介绍 34
4.2 电池包换电方式分析 34
4.3 单体可重构分析 35
第5章总结与展望 37
5.1 总结 37
5.2 展望 37
参考文献 39
致谢 40
|















