四环素类抗生素在白萝卜中的迁移累积规律研究(5500字)
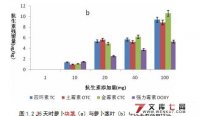
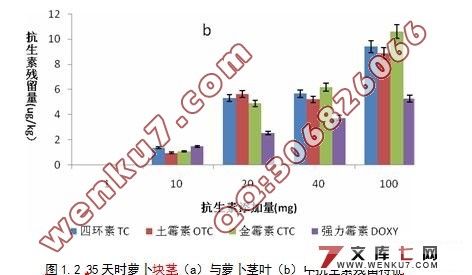
摘 要:本文通过半自然状态下的盆栽试验,以白萝卜为受试作物,研究了畜禽粪便中四环素类抗生素物质在农业生产中向植物体内迁移累积的规律。结果表明:当通过 猪粪使用带入土壤中的四环素类抗生素达到20 mg/m2 土地时,50d收获时4种抗生素(土霉素、四环素、金霉素、强力霉素)在萝卜块茎及茎叶中均有残留,在茎叶中其最大浓度分别为:14.39ug/kg、 13.93ug/kg、17.30ug/kg、8.86ug/kg,在根中其最大浓度分别为9.02ug/kg、11.49ug/kg、9.86ug /kg、3.4ug/kg。作物中四环素类抗生素残留浓度与土壤中的浓度成显著正相关,同时,作物中抗生素累积浓度随着作物生长时间的增加而升高,当通过 猪粪带入土壤中的四环素类抗生素为100 mg/m2 土地时,50 d采集的萝卜块茎中四环素、土霉素、金霉素及强力霉素比35 d采集的萝卜块茎中4种抗生素的含量分别增加了0.88、1.21、0.68和0.34倍;萝卜茎叶中4种抗生素则分别增加了0.48、0.62、 0.63及0.68倍,说明萝卜在生长的后期(35-50 d)比生长前期(0-35 d)更快地吸收累积抗生素。研究结果证实了有机肥源抗生素可通过农业生产进入农作物体内,给人类健康带来潜在不可预知的危害。
关键词:四环素类抗生素;白萝卜;累积规律;茎叶;块茎
Study on the tetracycline antibiotics accumulation rule in white turnip
Abstract:A pot experiment in the semi-natural state was conducted to investigate the possible pathways through which tetracycline antibiotics were accumulated in white turnip plants.The results showed that, when the concentration of the tetracycline antibiotics in the soil came to 20mg/m2, 50d harvest, the four antibiotics(oxytetracycline,tetracycline ,chlorotetracycline, doxycycline) all have remianed in stem and tuber of the white turnip. In the roots its largest concentration respectively were 14.39 ug/kg,13.93 ug/kg, 17.30ug/kg and 8.86ug/kg, and in the root, the largest concentration respectively were 9.02ug/kg,11.49ug/kg,9.86ug/kg,3.4ug/kg. The concentrations of tetracycline antibiotics in both shoots and roots were positively related to those in the soil. Meanwhile, it was found that the tetracycline antibiotics uptake by white turnip increased with the crop growth time increasing. when the concentration of the tetracycline antibiotics in the soil came to 100 mg/m2, the contents of the oxytetracycline, tetracycline, chlorotetracycline and doxycycline in 50d white turnip tuber were respectively increased 0.88,1.21, 0.68 and 0.34 times compared with that in 35d white turnip tuber; these four antibiotics in white turnip stems and leaves were respectively increased 0.48, 0.62,0.63 and 0.68 times. This showed that in the late growth stage (35-50d), the turnip absorbed the accumulated antibiotics faster than in the early period of the growth (0-35 d). The research results confirmed that the antibiotics could enter into the crops through agricultural production, and bring potential unpredictable danger to human health.
Key words: tetracycline antibiotics; white turnip; accumulation rule; stem; tuber
|