柴油机活塞的专用夹具设计(含选题审批表,任务书,开题报告,中期检查表,论文说明书9800字,CAD图纸7张)
摘 要:本设计通过对柴油机铝活塞加工技术的发展、活塞的工作环境以及结构特点的分析,确定了解放牌铝活塞的加工过程及加工方案,其中主要包括:生产纲领和生产类型的确定、材料的选择、毛坯的制造方法、机械加工余量的确定、各加工工序切削用量的确定、工序时间的计算以及工序卡片的编制。机械产品的生产过程是一个复杂的过程。机械制造工艺是机械制造方法和过程的总称。而生产过程中改变生产对象的形状、尺寸、相对位置和性质等,使其成为成品或半成品的过程,则称为工艺过程,是生产过程中的主要部分。按照零件的分析,基面的选择,选定的工艺路线,设计专用夹具的程序,完成本次毕业设计, 经过设计分析和论证,解放牌铝活塞的工艺设计与夹具设计是可行的。
关键词:活塞;工艺设计;夹具设计
Design Of Diesel Engine Pieton Special Fixture
Abstract: In the paper of this graduation design,through the comprehensive explication of the developing of the JieFang aluminum piston of the internal-combustion engine whose the machining technologies,the surrounding of working and the analysis of structural of the piston.It is conformed the technology process and arrange for process of piston.It mainly includes:produce outlines and produce types to be conformed,choose materials,the manufacturing methods of the semi-finished products of materials,the amount of remaining of machine process to be conformed,the cutting dosage of each process to be conformed,calculated the working procedure time and drew up the working procedure.The mechanical production process is a complex process. The machine manufacture craft is the machine manufacture method and the process always called. But in the production process changes the production object the shape, the size, the relative position and the nature and so on, causes it to become the end product or the half-finished product process, then is called the technological process, is in the production process main part. According to the components analysis, the basic plane choice, the working procedure route which designed, designs the jig the procedure, cost design, through the analysis and argument,the arts and crafts design and the tongs design of the piston is viable.
Key words: Piston;Working procedure;Machine tongs;Manufacture process technology
设计题目:活塞的机械加工工艺设计及夹具设计,
设计粗镗销孔夹具
设计要求:成批大量生产 手动夹紧 通用设备+专用工装 工序分散原则 常规工艺
设计内容:1、分析活塞零件图;
2、绘制活塞零件图(1张);
3、编写工艺过程卡片和工序卡片(一套);
4、绘制夹具总装图(2张);
5、绘制夹具零件图(2张);
6、设计计算说明书。
3 对解放牌铝活塞进行工艺分析
3.1 活塞的作用
由于柴油的物理化学特性,所以柴油机的构造是一个非常复杂的系统。而油缸就是这个系统中一个很关键的部位,对整个动力系统起着决定性影响,在某种意义上来说它是柴油机里面的“心脏”,而活塞则是柴油机里“心脏中的心脏”。活塞位于发动机气缸内,作往复运动,当燃烧室里的混合气体(空气和燃料)点燃并膨胀时,活塞受到气体的压力,气缸内混合气的燃烧压力为6~9MPa,并经过活塞销及连杆将压力传送给曲轴。气体的吸入,压缩,废气的排除,也都由活塞的运动来完成。活塞顶面受燃气的作用,所以顶面温度较高,活塞沿高度方向上的温度梯度也较大。因此活塞工作的主要特点是在高温、高压、高速及交变负荷下工作的,而且工作时的润滑条件极差。为了提高活塞的工作性能和寿命,它必须具有如下的要求:
① 在高温高压下具有足够的强度和刚度;
② 较轻的结构重量;
③ 良好的耐磨性和耐蚀性;
④ 良好的导热性,热膨胀系数小;
⑤ 保证气缸内部空间密封。
本次设计加工的是解放牌柴油机中的铝活塞。

目 录
摘要………………………………………………………………………………1
关键词……………………………………………………………………………1
1前言………………………………………………………………………………2
2设计任务……………………………………………………………………3
3对解放牌铝活塞进行工艺分析………………………………………………4
3.1活塞的作用………………………………………………………………4
3.2活塞工作条件及结构特点………………………………………………4
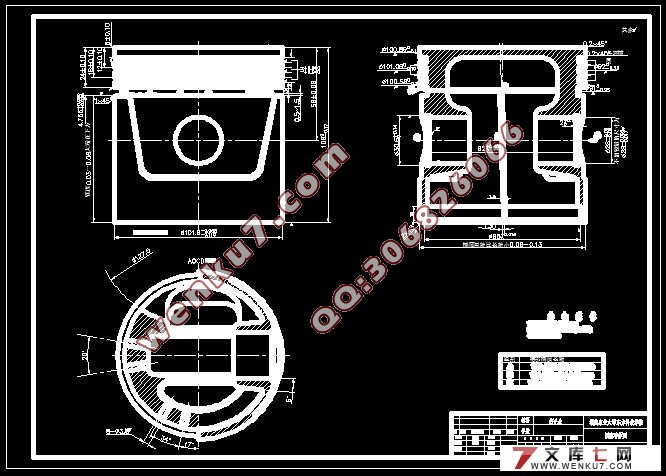
3.3活塞的主要技术要求……………………………………………………6
3.3.1活塞裙部外圆尺寸精度与表面粗糙度……………………………6
3.3.2活塞销孔精度与表面粗糙度………………………………………6
3.3.3活塞销孔位置精度…………………………………………………7
3.3.4活塞环槽的技术要求………………………………………………7
3.3.5活塞重量的要求…………………………………………………7
4 解放牌铝活塞工艺规程的设计及其加工…………………………………7
4.1活塞的材料及毛坯的制造………………………………………………7
4.2定位基准的选择………………………………………………………8
4.2.1精基准的选择……………………………………………………9
4.2.2粗基准的选择………………………………………………………10
4.3活塞的加工………………………………………………………………10
4.3.1考虑能否采用分组装配……………………………………………10
4.3.2加工方法的选择…………………………………………………11
4.3.3考虑工序的次序以及工序的集中分散程度…………………11
4.4确定工艺路线…………………………………………………………11
4.5机械加工余量、工序尺寸及毛坯尺寸的确定………………………11
4.5.1止口的加工余量…………………………………………………12
4.5.2端面及顶面的加工余量……………………………………12
4.5.3销孔的加工余量……………………………………………12
4.5.4外圆的加工余量………………………………………………12
4.6重点工序的加工说明………………………………………………………12
4.6.1止口的加工……………………………………………………12
4.6.2环槽的加工………………………………………………………14
4.6.3活塞裙部外圆的加工…………………………………………16
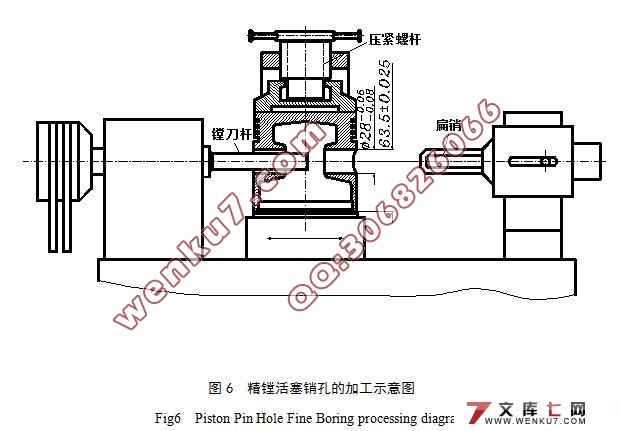
4.6.4销孔的加工…………………………………………………………16
4.7确定切削用量及基本工时(重点工序)………………………………18
4.7.1加工条件…………………………………………………………19
4.7.2计算切削用量……………………………………………………19
4.7.3基本工时……………………………………………………………19
4.8活塞的检验………………………………………………………………19
4.8.1裙部直径和椭圆度的测量…………………………………………20
4.8.2销孔轴心线与裙部轴心线的对称度的测量……………………21
4.8.3销孔轴心线对裙部轴心线的垂直度的测量………………………22
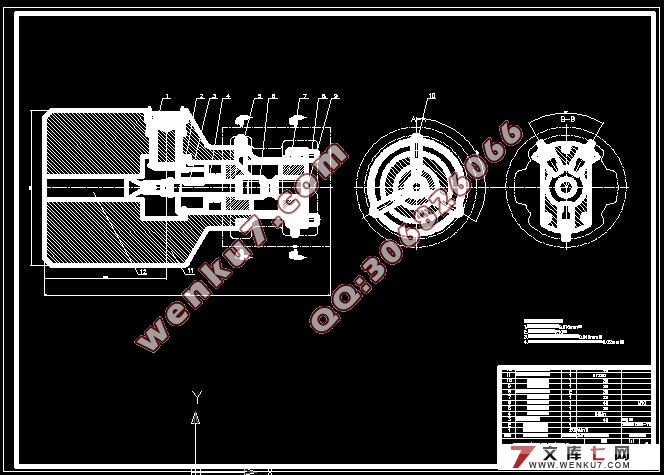
5专用夹具的设计…………………………………………………………………23
5.1问题的提出…………………………………………………………………23
5.2夹具的设计…………………………………………………………………24
5.2.1精车外圆夹具设计…………………………………………………24
5.2.2粗镗销孔夹具设计………………………………………………24
5.3切削力和夹紧力的计算和校核……………………………………………25
5.3.1切削力………………………………………………………………25
5.3.2夹紧力………………………………………………………………26
6结论…………………………………………………………………………27
参考文献 ………………………………………………………………………27
致谢………………………………………………………………………………28
附录………………………………………………………………………………28
|