某汽车发动机曲轴加工工艺及夹具设计(含CAD图,工艺工序卡)(选题审核表,任务书,开题报告,外文翻译,论文说明书17000字,CAD图10张)
摘要
在机械领域中,发动机曲轴是一类常用而且重要的曲轴类零件,其作用是连接和传递,特别是在连接过程中轴颈磨损,因此曲轴承受多变载荷,在保证优良的结构设计以外,零件材料、工艺设计和夹具设计都是重要的组成环节。零件的技术要求相对较高,但自身的刚度较差,容易产生变形,此外,毛坯制造形式和热处理方式对其机械性能影响尤为明显,因此,加工过程中,必须将粗精加工分开进行。完整的工艺规程制定以及夹具设计是保证零件功能完整性、安全可靠性以及生产成本最小化的关键所在。该发动机曲轴的工艺设计包含材料分析和选用、确定毛坯的制造形式和热处理方式、钻孔、扩孔、绞孔、车销等以及专用夹具设计的详细流程,不断学习和完善机械相关专业知识技能。
关键词
发动机曲轴;工艺分析;工艺规程;夹具设计
Abstract
In the mechanical field, the engine crankshaft is a kind of common and important crankshaft parts. Its function is connection and transmission, especially the journal wear in the connection process. Therefore, the crankshaft bears variable load. In addition to ensuring excellent structural design, the part material, process design and fixture design are important components. The technical requirements of the parts are relatively high, but the rigidity of the parts is poor, which is easy to produce deformation. In addition, the influence of the blank manufacturing form and heat treatment mode on their mechanical properties is particularly obvious. Therefore, in the process of machining, the rough and finish machining must be carried out separately. Complete process planning and fixture design are the key to ensure the functional integrity, safety and reliability of parts and minimize the production cost. The process design of the engine crankshaft includes material analysis and selection, determination of the manufacturing form and heat treatment method of the blank, drilling, reaming, reaming, turning pin, etc. as well as the detailed process of special fixture design, and continuous learning and improvement of mechanical related professional knowledge and skills.
Keywords :Engine crankshaft; Process analysis; Process specification; Fixture design
2.1 零件的作用
曲轴是发动机的一部分,也是零件当中最重要的零件之一。作用主要是承受来自连杆的轴向力。将其变为动力。曲轴承受旋转质量的离心力、周期变化的气体惯性力和往复惯性力的共同作用,承受弯曲扭转载荷的作用。
2.2 零件的技术要求分析
2.2.1 发动机曲轴零件材料的分析
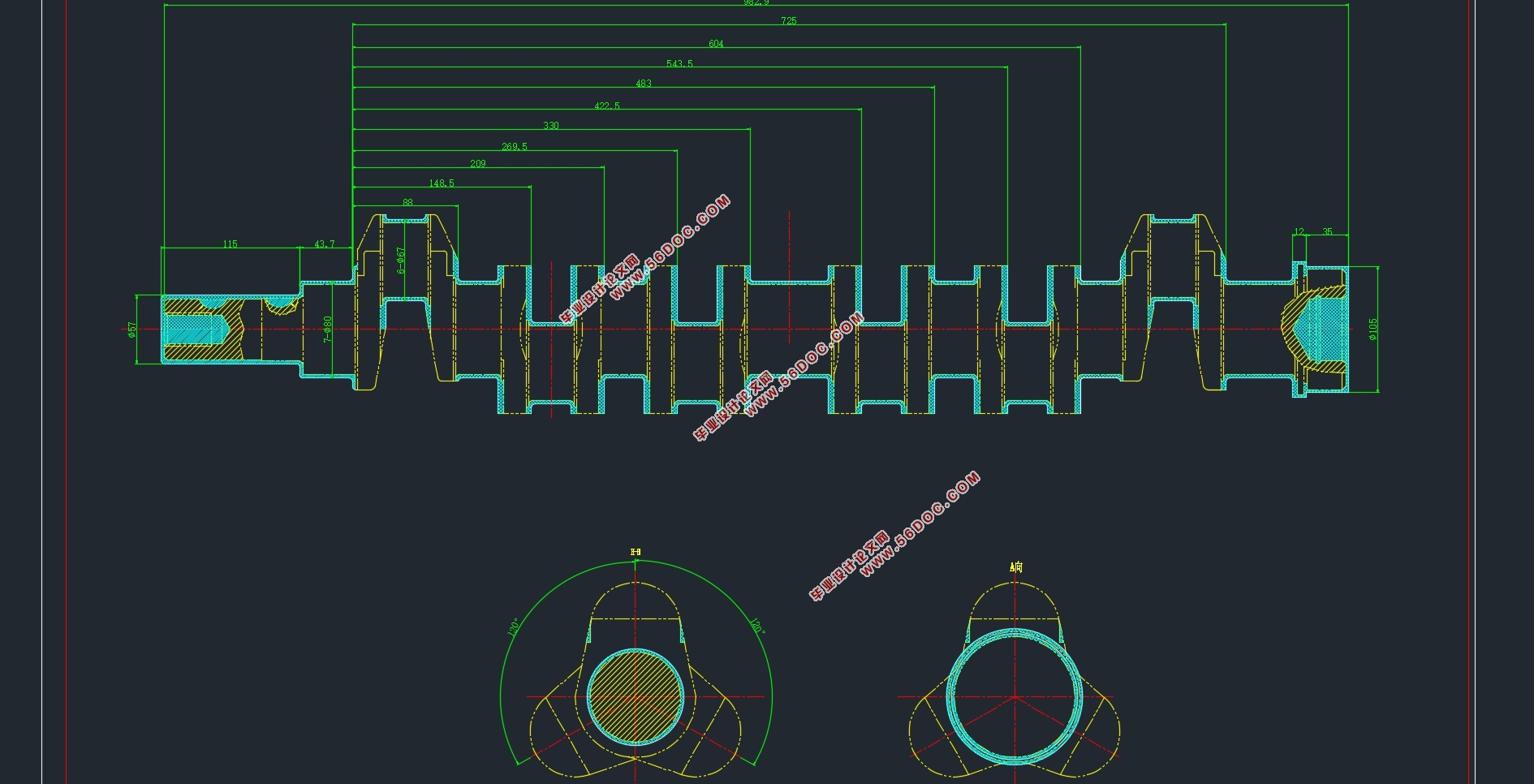
图 2.1 CAD 零件图确定此零件是异形轴类零件。此零件材质为45钢。是碳素结构钢。
2.2.2 加工表面的粗糙度
左端Φ50 外圆加工表面为去除材料得到的粗糙度为Ra0.8m ;右端Φ100 外圆加工表面为去除材料得到的粗糙度为Ra0.8m 等。此外其他的加工表面有Ra0.4m 、Ra1.6m 等加工表面。由于此零件的工作环境确定此曲轴的转速高达6000r / min 。所以个加工表面要求高。加工难度大。
2.2.3 结构工艺性分析
曲轴支撑着其它转动件回转并传递扭矩,同时又通过轴承与机器的机架连接。其长度大于直径,由外圆柱面、螺纹及相应端面所组成。加工表面通常除了外圆表面、螺纹、端面外,还有内孔。
此零件为四拐曲轴,曲轴的形状较为复杂,全部连杆轴颈为Φ62 外圆,多拐的轴线相对夹角为 120°。能够以外圆定位,并降低同轴度误差。且所有孔和所有外圆的轴线和端面垂直。存在槽和阶梯孔,易于排除废屑,因此能够发现该零件的内孔、端面和台阶孔使其他工序内容便于加工。
可以确定内孔的轴线、外圆的轴线都与端面相垂直,便于进刀退刀加工。两端面打中心孔,辅助定位,容易加工。
各尺寸精度要求达到一般尺寸公差,标注正确。

目录
1 序 言 1
2 零件的工艺性分析 1
2.1 零件的作用 1
2.2 零件的技术要求分析 2
2.3 零件加工要求分析 3
3 工艺规程设计 5
3.1 毛坯的制造方法 5
3.2 毛坯图的绘制 5
3.3 定位基准的选择 6
3.4 加工顺序的安排 6
3.5 拟定加工工艺路线 7
3.6 加工余量及工序尺寸的确定 9
3.7 加工设备的选择 9
3.8 刀具的选择 10
3.9 切削用量和基本工时 11
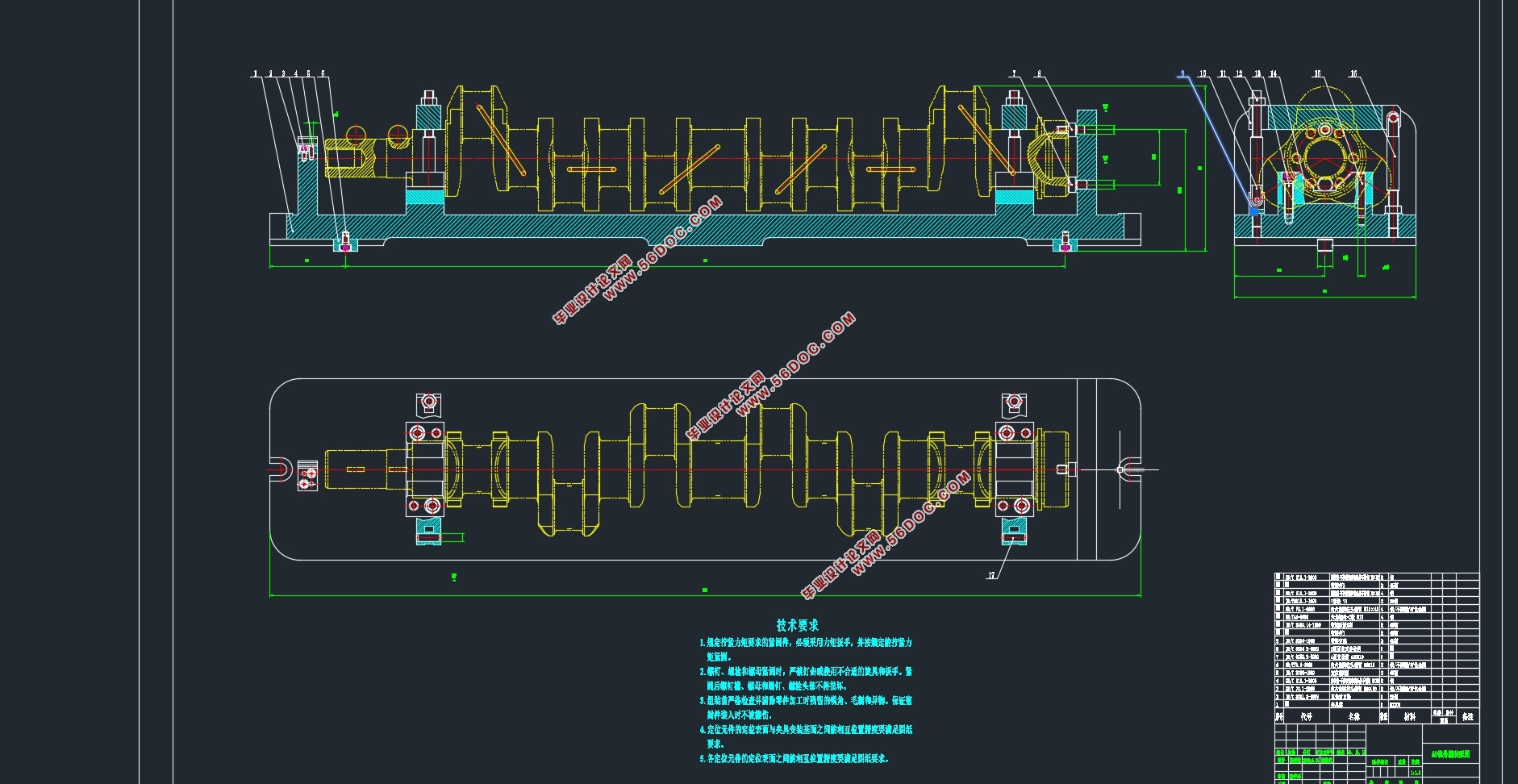
4 夹具设计 23
4.1 定位方案设计 23
4.2 夹紧方案 25
4.3 定位误差分析 25
4.4 切削力和夹紧力的计算 26
4.5 主要零部件设计 27
4.5.2 夹具体 28
5 结论 29
参考文献 29
致谢 30
附 录 31
|









