电力线感应取电电磁仿真与实现(任务书,开题报告,外文翻译,论文9000字)
摘 要
感应取电供能是一种非常好的供能方式,相较与单独电池供能、太阳能供能、激光供能等供能方式有着其不可忽视的优点,随着智能电网的发展,感应取电供能方式广泛应用与电网上检测设备的供电,电流互感器加上后续的保护与处理电路能够从母线上获取稳定的电流,为负载端设备的正常运行提供良好的保证。
本文首先介绍了感应取电供能方式的研究背景,通过与其他几种不同的供能方式对比,说明研究感应取电供能方式的必要性。之后,陈述了与感应取电相关的基本原理,介绍了电流互感器的结构和工作原理,说明磁芯的作用、特性与相关参数,仿真分析磁芯中磁力线的分布,讨论了取能电源功率与各参数间的关系。最后介绍了保护与处理电路的相关设计,包括冲击保护电路、整流电路、滤波电路和稳压电路。
关键词:感应取电;电流互感器;仿真
Abstract
Induction power supply is a very good way of energy supply. Compared with the single battery, solar energy and laser energy supply, it has its own merits that can not be ignored. With the development of smart grid, induction power supply is widely used and the power supply of detection equipment in power grid. Current transformer and subsequent protection and processing circuit can obtain stability from busbar. Current, for the normal operation of load terminal equipment to provide a good guarantee.
Firstly, this paper introduces the research background of induction power supply mode, and illustrates the necessity of studying induction power supply mode by comparing with other different energy supply modes. Afterwards, the basic principles related to induction charging are stated, the structure and working principle of current transformer are introduced, the function, characteristics and relevant parameters of magnetic core are explained, the distribution of magnetic lines in magnetic core is simulated and analyzed, and the relationship between the power of power supply and parameters is discussed. Finally, the design of protection and processing circuit is introduced, including impulse protection circuit, rectifier circuit, filter circuit and voltage stabilization circuit.
Key words: induction charging; current transformer; simulation
目录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景及意义 1
1.2 论文研究内容与目的 3
1.3 本章小结 3
第2章 电力线感应取电理论分析 4
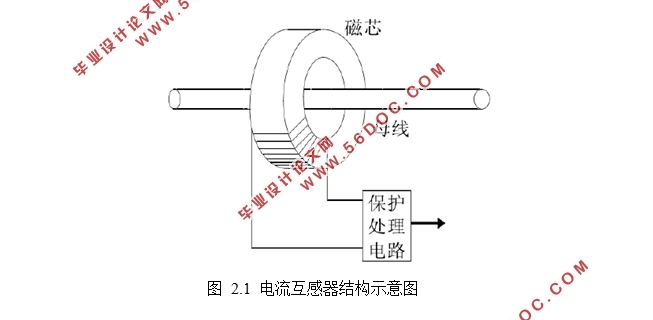
2.1 电流互感器的基本结构 4
2.2磁芯介绍 4
2.2.1 磁芯的作用 4
2.2.2 磁芯的性质 5
2.2.3 磁芯材料的选择 6
2.3 电流互感器的基本原理 6
2.4 磁芯气隙对磁芯性能的影响 9
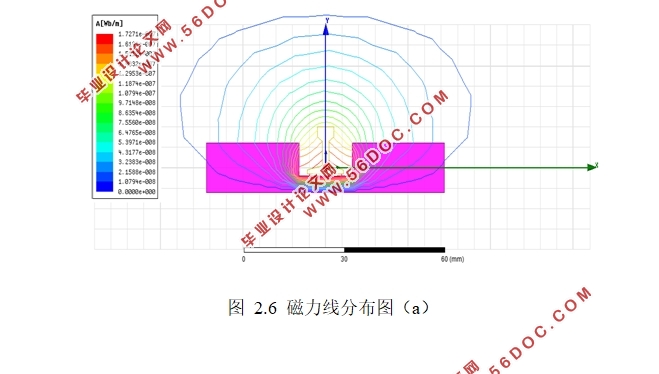
2.5 U型取电磁芯形状设计与电磁分布 10
2.6 U型取电磁芯相关参数计算 11
2.7 本章小结 12
第3章 保护与处理电路 13
3.1 保护电路的设计 13
3.2 整流电路的设计 14
3.3 滤波电路的设计 16
3.4 稳压电路的设计 17
3.5 本章小结 18
第4章 结论与展望 19
参考文献 20
致谢 21
|





