基于PID控制的1/4车辆主动悬架仿真研究(任务书,开题报告,外文翻译,论文设计说明书24000字)
摘 要
悬架是一个关键组成部分,汽车零部件,从而保证身体或车轮与主机系统之间的弹性接触,并可以传输负载,缓解冲击,振动和调整车身状态的衰减,直接影响到汽车的乘坐舒适性和操纵稳定性。
随着人们对现代汽车乘坐舒适性和行驶安全性的要求愈来愈高,设计一个综合性能良好的悬架,已成为现代汽车研究的一个侧重的课题。传统的被动悬挂系统弹性构件刚度和阻尼减震元件是不变的,汽车行驶的路况,负载变化和其他因素的影响,因此,必须制定一个被动悬架不同的新的悬挂。主动悬架是基于现代控制理论和电子技术的发展和开发,与车辆的运行状态,可以自适应地改变其刚度和阻尼参数,具有优良的阻尼性能和操纵稳定性,未来汽车吊框架的一个重要研究方向。
本论文先根据牛顿定理,运用车辆动力学理论,建立了被动悬架和二自由度1/4主动悬架系统的动力学模型。并建立了路面输入分别为:白噪声信号、阶跃信号以及正弦信号的路面不平度数学模型。同时,概述了悬架性能的三个评价指标,即车身加速度、悬架动挠度、轮胎动载荷。并利用软件Matlab/Simulink构建出汽车悬架控制系统仿真模型图,包括路面输入模型,被动悬架模型,PID控制主动悬架模型。运行仿真模型图即可实现不同路面输入信号的悬架系统的仿真。最后,对悬架性能评价指标的仿真结果进行分析。
关键词:主动悬架;MATLAB;建模;PID控制;仿真
Abstract
Suspension is an component of the important assembly of the automobile, it guarantees to contact with a flexible between the wheels or axles and bearing system, and can transfer loads、relax impulsion、reduce vibration and regulate the body position of the vehicle in traffic, and have a direct impact on ride comfort and operate stability.
With the increasing requirement of the vehicle's ride comfort and road security, the design of suspension with good performance has become more and more important. As a traditional passive suspension having a constant spring stiffness and damper coefficient which is not interfering with the road surface and the load change, so it is necessary to design a new style suspension. Active suspension and modern control theory and development of electronic technology, and its stiffness and damping coefficients can prosper, to adapt to different working environment, improve vehicle ride comfort and road holding. So it is significant to research and develop active suspension.
Firstly, according to the Newton theorem, the paper use the vehicle dynamics theory, and set up the dynamics model of the passive suspension and the second freedom active suspension system based on 1/4 of the body. And translate the differential equations into a form of expression of the state equations. And establish the road roughness mathematical model of the road input signal for sine, step random and white noise signal, and achieve the simulation. At the same time, outlined the three evaluation index of the suspension performance, such as the body vertical acceleration, the relatively dynamic load of the wheel, the suspension dynamic deflection. And build the simulation model plans of the control system of the automobile suspension by the Matlab/Simulink software, including the importable model of the road, the passive suspension model, the active suspension model of the PID control. And run the simulation model map to achieve the simulation of the different input signal of the suspension control system. Finally, analysis the simulation results of the evaluation index of the suspension performance .
Key words: Active suspension; MATLAB; Modeling; PID control; Simulation
本论文主要研究内容
本论文研究的是基于两自由度1/4车辆主动的悬架的在PID控制策略下进行仿真研究,以l/4主动的悬架为研究的对象,建立l/4主动悬架数学简化模型,在对被动悬架和PID控制的主动悬架进行比较分析,研究的主要内容包括:
1、建立1/4悬架数学模型
结合汽车悬架的实际情况,学习并运用运动学和动力学及车辆构造相关理论,对汽车悬架系统进行简化分析,建立两自由度1/4主动悬架数学模型。根据牛顿第二定律,在对其在受力分析的基础上建立动力学方程,并以此作为控制策略仿真的基础。
2、建立路面路谱模型,提出悬架性能的评价标准
考虑到路面激励对悬架控制的重要影响,将路面激励信号结合系统仿真模型。在振动方面使用白噪声信号来模拟实际的持续的小的不平整路面;在冲击方面使用阶跃与正弦来模拟实际凸起和凹坑。
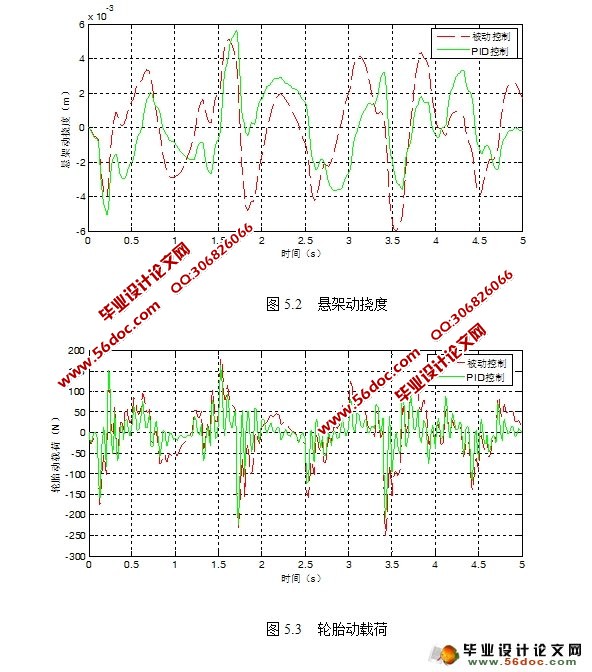
根据车辆设计要求的平顺性和操纵稳定性。选择悬架的评价参数为;车身加速度用于表示车辆行驶的平顺性效果;悬架动挠度和轮胎动载荷用于表示车辆操纵稳定性效果。
3、选定控制方法并设计控制器
结合经典控制理论和现代控制理论,本文采用具有实际应用价值的PID控制,根据其原理设计其控制器。
4、建立仿真模型
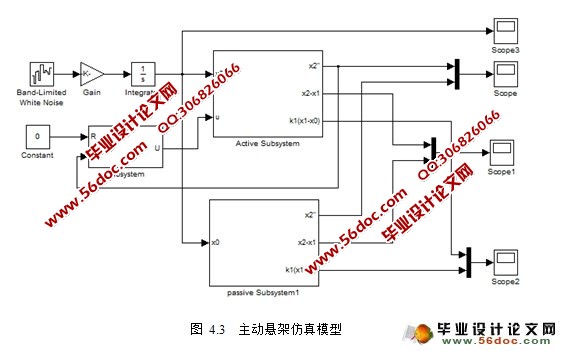
根据建立的悬架系统的控制原理图,在Matlab仿真软件建立汽车主、被动悬架、PID控制器仿真模型,然后对主、被动悬架的性能分析对比。
5、仿真结果分析
参照车辆设计要求的平顺性和操纵稳定性,以车身加速度、悬架动挠度和轮胎动载荷值作为主要评价指标,通过对三种输入信号下的控制策略仿真曲线进行分析比较,归纳总结出控制策略的优缺点以及可行性与有效性。
目 录
摘 要 III
Abstract IV
目 录 V
VI
1 绪 论 1
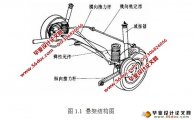
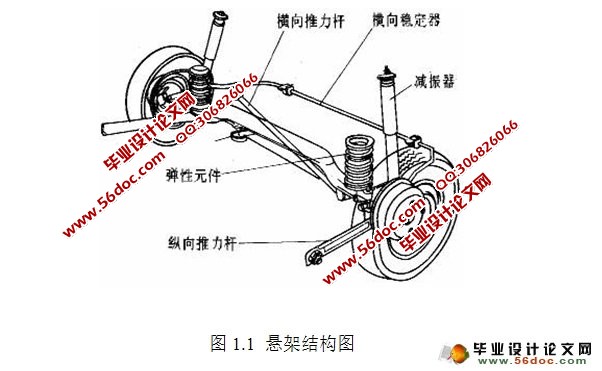
1.1 悬架系统介绍 1
1.1.1 悬架的功能 1
1.1.2 悬架的分类 1
1.2 主动悬架控制理论研究的目的和意义 4
1.3 国内外主动悬架理论研究动态 4
1.3.1 国内外主动悬架的理论 4
1.3.2 国内外主动悬架的应用 5
1.3.3 国内外主动悬架研究趋势 5
1.4 本论文主要研究内容 6
2 汽车悬架平顺性评价方法 8
2.1 汽车平顺性概述 8
2.1.1 汽车平顺性的研究发展概况 8
2.2 影响汽车平顺性的因素 10
2.2.l 路面不平度统计特性的研究 10
2.2.2 影响平顺性的车身部件的研究 10
2.3 汽车平顺性评价方法 11
2.4 汽车悬架系统的评价指标 12
3 主动悬架控制系统的动力学模型 13
3.1 主动悬架的数学模型 13
3.1.1 概述 13
3.1.2 两自由度主动悬架的动力学模型 14
3.2 路面路谱模型建立 16
3.2.1 路面不平度的功率谱 17
3.2.2 空间频率谱函数与时间频率谱函数的转化 18
4 基于1/4主动悬架系统模型的PID控制 21
4.1 主动悬架PID控制理论 21
4.1.1 PID控制 21
4.2 PID控制器的参数整定 24
5 系统的计算机仿真结果与分析 26
5.1 仿真环境Matlab/Simulink简介 26
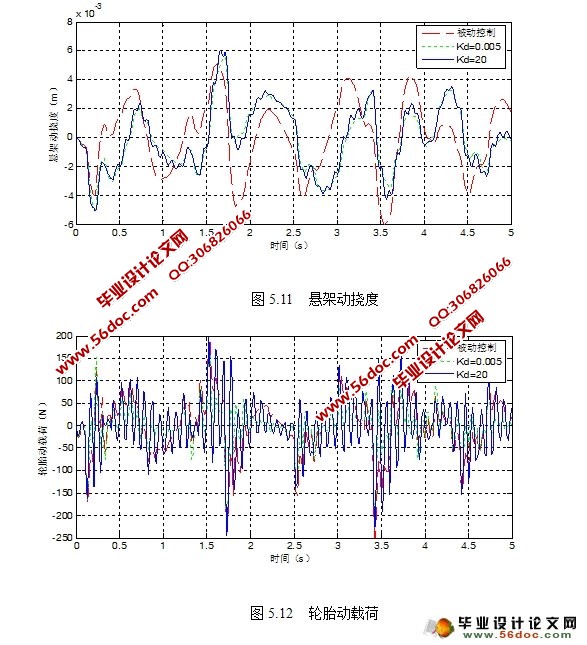
5.2 仿真实验和结果分析 27
5.2.1 白噪声信号下的比较: 27
5.2.2 阶跃信号下的比较: 34
5.2.3 正弦信号下的比较: 41
6 总结和展望 49
6.1 总结 49
6.2 不足之处和展望 49
致 谢 51
参考文献 52
附 录 53
|