基于单片机的温控风扇设计(任务书,开题报告,外文翻译,论文14000字)
摘 要
传统风扇只能依靠手动调节控制风速,夏夜入眠后,过大的风速极易导致受凉感冒,此时设计一款根据实时温度自动调节风速的风扇,既能为生活带来便利又有助于节能环保。
本设计是一款基于STC89C51单片机的小型智能温控系统,采用高精度温度传感器DS18B20进行环境温度测试。通过LCD1602显示温度值,系统设置3个按钮,用户可以通过其中一个按钮进入设置模式,另两个按钮的作用是调整温度的上限值和下限值。通过将数据存储在单片机中的EEPROM中实现断电存储。
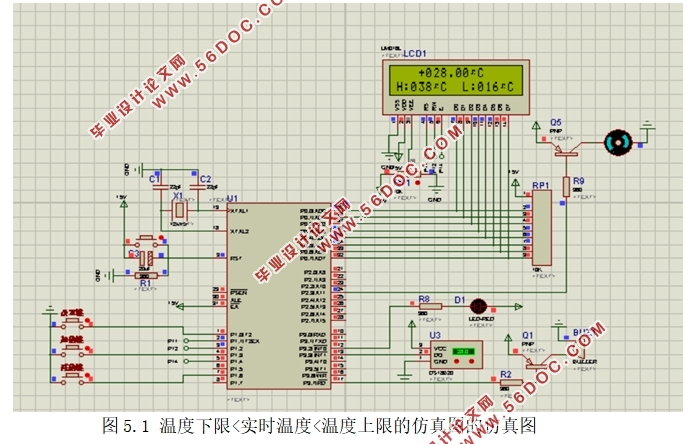
当实时温度低于下限时,蜂鸣器鸣响起,LED灯亮起,风扇停止。当采集的温度在上限和下限温度之间时,蜂鸣器和LED灯停止工作,并且风扇进入小风力模式。当实时温度高于设置温度上限,蜂鸣器响起,LED灯亮起,风扇进入大风模式。
关键词:实时温度;STC89C51;风扇
Abstract
Fan can only rely on traditional manual regulation control wind, summer night to sleep, too easily lead to catch cold catch cold catch a cold, the wind speed at this point design according to the real-time temperature automatically adjust the wind speed of the fan, both can bring convenience for life and contribute to energy conservation and environmental protection.
This design is a small intelligent temperature control system based on STC89C51 single chip microcomputer. It adopts the high-precision temperature sensor DS18B20 for environmental temperature testing. LCD1602 shows the temperature value, and the system sets three buttons. The user can enter the setting mode through one of them. The other two buttons are used to adjust the upper and lower temperature limits. The data is stored in the EEPROM in the MCU to realize the storage of power off.
When the real-time temperature is lower than the lower limit, the buzzer rings, the LED lights are on, and the fan stops running. When the collected temperature is between the upper and lower limits, the buzzer and LED lights stop working, and the fan enters the small wind mode. When the real-time temperature is higher than the set temperature ceiling, the buzzer rings, the LED lights are on, and the fan enters the large wind mode.
Key Words:Real time temperature; STC89C51; fan
本文的研究内容和组织结构
本设计的重点是将单片机原理与电机驱动结合起来,实现智能温控。本设计采用STC89C51为主要的微处理器,结合数字温度传感器DS18B20和液晶显示器LCD1602,完成对温度的实时监控,并且能够通过预设温度与实际温度的比较,判断该温控系统控制的风扇需要进入的工作状态。本设计能够手动调节预设温度,并且断电后能保存上一次设置的温度值。
论文的总体框架如下:
第一章为绪论,介绍了温控风扇设计的背景,并对国内外的研究现状做出了阐述。
第二章为整体方案设计,对每个模块的硬件选型进行了论证,选出了最符合设计初衷的方案。
第三章为单元模块电路设计。介绍了单元模块电路的设计原理,说明了每个模块电路在设计中的作用。
第四章为软件设计。主要从软件设计方面,利用流程图说明了主程序和各个子程序的设计思想,并对部分代码做了具体介绍。
第五章为系统调试,从软件和硬件两个方面,对实物进行了测试,并解决了存在的问题。
第六章为总结与展望。总结了本论文的研究过程和研究的内容,并展望了智能温控风扇的下一步研究方向。
系统整体结构
本设计为智能温控风扇,分为单片机模块、测温模块、温度显示模块、驱动电机模块、按键输入模块共5个模块

目录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 设计的目的及意义 1
1.2 国内外研究现状 1
1.3本文的研究内容和组织结构 1
第2章 温控风扇整体方案设计 3
2.1系统整体结构 3
2.2硬件选型 3
2.2.1 主控芯片的选择 3
2.2.2 显示器件的选择 4
2.2.3 温度传感器的选择 5
2.2.4 调速方式的选择 5
2.3 系统总体方案 6
第3章 温控风扇单元电路设计 7
3.1 单片机最小系统电路 7
3.1.1 STC89C51单片机 7
3.1.2 STC89C51 单片机最小系统设计原理 8
3.2 温度采集电路的设计 9
3.2.1 温度传感器 DS18B20 9
3.2.2 温度传感器的工作原理 10
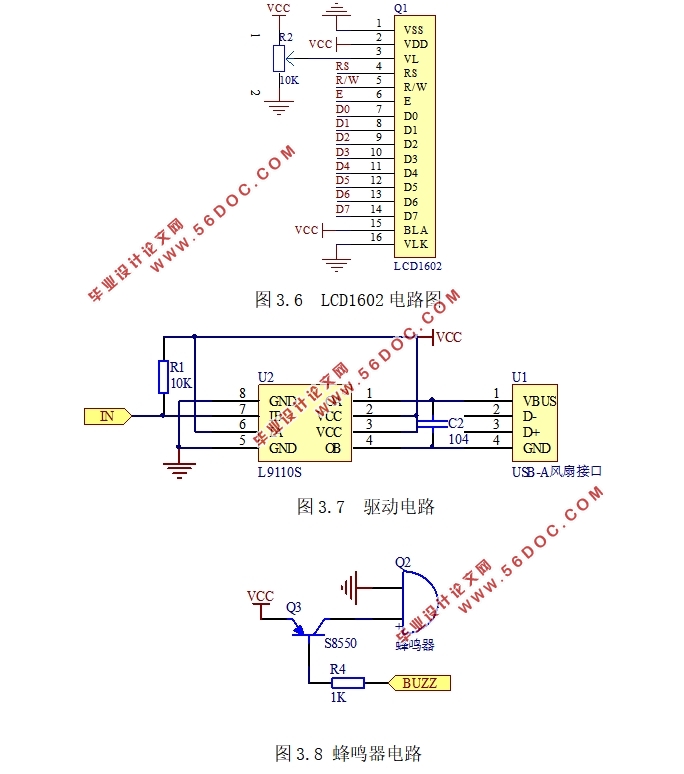
3.3 液晶显示电路的设计 11
3.3.1 LCD1602液晶显示器 11
3.3.2 液晶显示器工作原理 11
3.4 风扇驱动电路的设计 12
3.4.1 驱动芯片 L9110S 12
3.4.2驱动电路工作原理 12
3.5 蜂鸣器电路的设计 13
3.6 独立按键电路的设计 13
第4章 智能风扇软件设计 15
4.1 软件开发环境 15
4.2 智能风扇函数设计 15
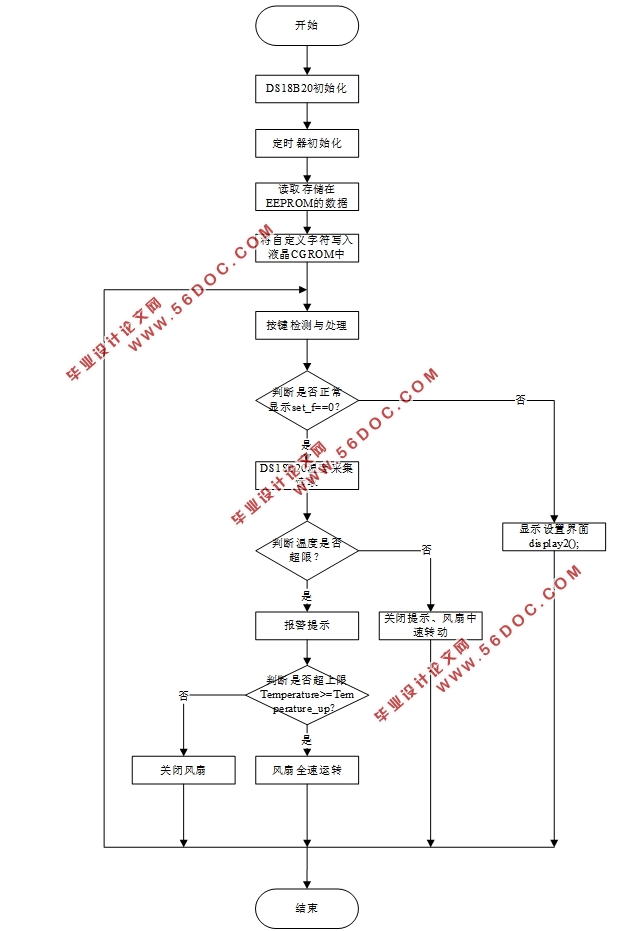
4.2.1 主函数设计 15
4.2.2 LCD1602显示函数的设计 17
4.2.3 DS18B20温度采集的函数设计 18
4.2.4 驱动电机模块的函数设计 20
4.3 软件调试 22
4.3.1 LCD1602液晶显示部分调试 22
4.3.2掉电存储部分调试 22
第5章 智能风扇系统仿真与实物测试 23
5.1 系统功能仿真 23
5.2 实物测试 25
5.2.1 系统硬件实物 25
5.2.1 按键显示部分测试 25
5.2.2 温度采集部分测试 26
5.2.3 驱动电机部分测试 27
5.3 系统功能 28
5.3.1 系统实现的功能 28
5.3.2 系统功能分析 28
第6章 总结与展望 29
6.1 本文工作总结 29
6.2下一步的工作展望 29
参考文献 30
致 谢 31
|









