基于单片机的PM2.5监测系统设计与开发(附程序代码,电路原理图)(任务书,开题报告,外文翻译,论文14500字,程序代码,电路原理图)
摘 要
PM2.5因其对人体健康危害大,影响范围广,近几年在中国引起广泛关注。各地政府监测的PM2.5数据虽然准确,但不能随时随地了解到身处环境的PM2.5浓度,因此有局限性。
本次设计的PM2.5遥测系统是基于光散射法以及基于MIE原理的算法来获取PM2.5浓度,系统主控芯片选择STC89C52RC单片机、GP2Y1010AUOF粉尘传感器获取的PM2.5模拟信号送给ADC0832转换之后再交给单片机计算与处理,并设有报警模块、按键设置模块、LCD1602显示模块以及GPRS无线模块。
本系统经过调试之后,能准确测出所处环境空气PM2.5的浓度,并能实现超标报警功能、报警值设置功能、PM2.5浓度实时显示功能以及向目标手机发送报警短信功能。表明本系统能实时监测PM2.5浓度并且实现远程监测。
关键词:PM2.5;监测技术;单片机;GSM;GP2Y1010AUOF
Abstract
PM2.5 because of its harm to human body health, influence range, caused wide public concern in recent years in China. Government around the monitoring of PM2.5 data accurate, but can't learn anytime and anywhere in the environment of PM2.5 concentrations, thus there are limitations.
PM2.5 telemetry system of this design is based on light scattering method and algorithm to get PM2.5 concentrations, on the basis of the principle of MIE system master control chip select STC89C52RC MCU, GP2Y1010AUOF dust sensors of PM2.5 analog signal sent ADC0832 again after conversion to the single-chip computer calculation and processing, and set alarm module, keys module, the LCD1602 display module and GPRS wireless module.
After debugging, this system can accurately measure the environment air PM2.5 concentrations, and can realize the excessive alarm function, the alarm value is set, PM2.5 concentrations of real-time display and send alarm messages to the target cell phones function. Show that the system can realize the remote real-time monitoring PM2.5 concentrations and monitoring.
Key Words:PM2.5;Monitoring technology;Single chip microcomputer;GSM;GP2Y1010AUOF


目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 设计目的与意义 1
1.2 国内外研究现状 2
1.2.1 国内外空气质量标准 2
1.2.2 国内外监测PM2.5主要方法及方案对比 2
第2章 系统的硬件设计 4
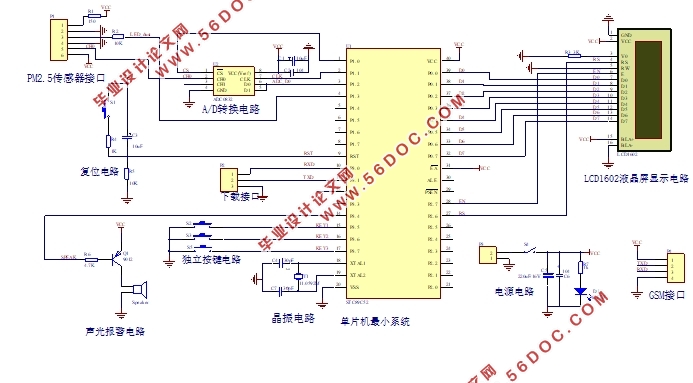
2.1 硬件的总体设计 4
2.2 单片机选型及外围电路设计 4
2.2.1 单片机选型 4
2.2.2 单片机最小系统 6
2.2.3 时钟电路 7
2.2.4 复位电路 7
2.2.5 定时器 8
2.3 AD转换芯片及电路设计 9
2.4 粉尘传感器及电路设计 11
2.5 液晶显示模块设计 14
2.6 按键模块设计 16
2.7 报警模块设计 16
2.8 电源模块设计 17
2.9 GSM模块设计 17
第3章 系统的软件设计 22
3.1 软件的总体设计 22
3.2 软件的开发环境 23
3.3 主程序的设计 23
3.4 GPRS无线模块程序设计 25
3.5 AD转换模块程序设计 26
第4章 系统调试 29
第5章 系统的误差分析和经济性分析 32
5.1 系统的误差分析 32
5.1.1 系统的误差来源 32
5.1.2 系统的误差校正 32
5.2 系统的经济性分析 32
第6章 总结与展望 34
参考文献 35
致谢 36
附录A 37
附录B 43
|







